We
use many aggregate functions like sum, count, average, min, and max. In LINQ we
can use this function in the following manner:-
SUM
If
we want to perform sum aggregate function then we will implement the following
queries:-
Sum with array
int[] marks
= new int[] { 23, 45, 78, 90, 56, 89, 10, 32 };
//simple sum without condition
int res =
marks.Sum();
//sum with condition
int
res_with_where = marks.Where(cond => cond > 50).Sum();
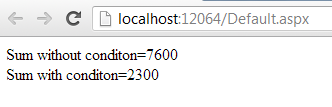
Response.Write("Sum without condition= " + res + "<br/>");
Response.Write("Sum with condition="+ res_with_where+"<br/>");
Output of this code as follows:-
Figure
1
Sum with Generics
List<data> dt = new List<data>()
{
new data{roll_no=1, student="isha",
per=100},
new data{roll_no=2, student="neha",
per=89},
new data{roll_no=3, student="rahul",
per=34}
};
int per_sum
= dt.Sum(x => x.per);
int
per_sum_with_conditon = dt.Where(stu => stu.student.EndsWith("ha")).Sum(x => x.per);
Response.Write("Sum
without condition= " +
per_sum + "<br/>");
Response.Write("Sum with condition=" + per_sum_with_conditon + "<br/>");
Output of this code as follows:-
Figure
2
Sum with database:-
DataContext dc = new DataContext("Data
Source=.;Initial Catalog=TechAltum;Integrated Security=True");
//sum without condition
int
sum_without_cond = dc.GetTable<Class1>().Sum(prod_sum => prod_sum.no_of_prod);
//sum with conditon
int
sum_with_cond = dc.GetTable<Class1>().Where(cond => cond.prod_year ==
2001).Sum(prod_sum => prod_sum.no_of_prod);
Response.Write("Sum
without conditon=" +
sum_without_cond + "<br/>");
Response.Write("Sum with conditon=" + sum_with_cond + "<br/>");
Output of this code as follows:-
Figure
3
Similarly
we can perform max, min, average and count using LINQ.
For
any query you can mail me at info@techaltum.com



best blog ever i read on great topic Travel Agency Database
ReplyDelete